Recent searches
Search options
It is a pleasure to announce the publication of this #review about recent advances in olive tree under salt stress. https://www.mdpi.com/2079-7737/14/3/287
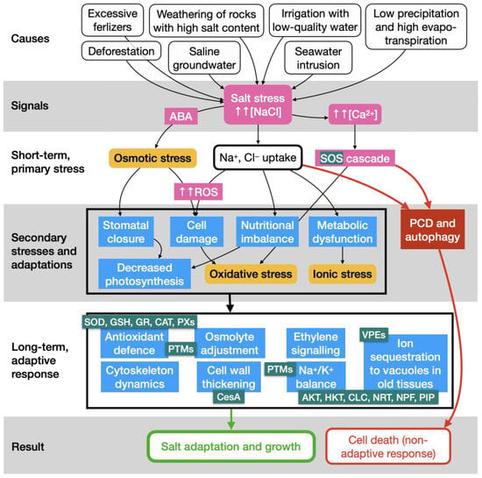
MDPIMulti-Omic Advances in Olive Tree (Olea europaea subsp. europaea L.) Under Salinity: Stepping Towards ‘Smart Oliviculture’Soil salinisation is threatening crop sustainability worldwide, mainly due to anthropogenic climate change. Molecular mechanisms developed to counteract salinity have been intensely studied in model plants. Nevertheless, the economically relevant olive tree (Olea europaea subsp. europaea L.), being highly exposed to soil salinisation, deserves a specific review to extract the recent genomic advances that support the known morphological and biochemical mechanisms that make it a relative salt-tolerant crop. A comprehensive list of 98 olive cultivars classified by salt tolerance is provided, together with the list of available olive tree genomes and genes known to be involved in salt response. Na+ and Cl– exclusion in leaves and retention in roots seem to be the most prominent adaptations, but cell wall thickening and antioxidant changes are also required for a tolerant response. Several post-translational modifications of proteins are emerging as key factors, together with microbiota amendments, making treatments with biostimulants and chemical compounds a promising approach to enable cultivation in already salinised soils. Low and high-throughput transcriptomics and metagenomics results obtained from salt-sensitive and -tolerant cultivars, and the future advantages of engineering specific metacaspases involved in programmed cell death and autophagy pathways to rapidly raise salt-tolerant cultivars or rootstocks are also discussed. The overview of bioinformatic tools focused on olive tree, combined with machine learning approaches for studying plant stress from a multi-omics perspective, indicates that the development of salt-tolerant cultivars or rootstocks adapted to soil salinisation is progressing. This could pave the way for ‘smart oliviculture’, promoting more productive and sustainable practices under salt stress.

